Lumbar area osteochondrosis is a disease that changes and destroys cartilaginous tissue of the intervertebral disc at the bottom.Without the cartilage, the distance between the vertebrae decreases significantly.And with a little sharp turn, they can switch.The main danger of the disease is the possibility of the formation of intervertebral hernia.
Don't you lean on to raise objects that have fallen to the floor?Do you have acute pain in the lumbar spine and often go, wrap the waist into a warm scarf?Don't ignore the situation that bothered you.
Lumbar region osteochondrosis can be dragged for a long time.No need to experience the body for strength.Love your body.And it will reply.
The lumbar region contributes most of the burden of all weight compared to the chest and cervical department.Therefore, these osteochondrosis subspecies are the most common.
What is the stage of development of osteochondrosis?
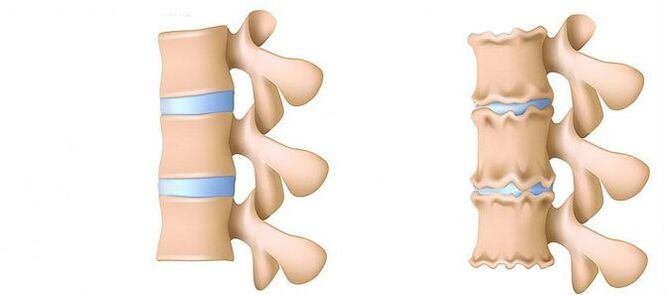
- Stage 1. Previously.The height of the disc is reduced.In the fibrous ring (the outer layer of the intervertebral disc from the cartilagin fiber) is formed.The lumbar muscles start to get tired quickly.You feel uncomfortable in the back.
- Level 2. Violation of the metabolic process in the core jacket (the center of the intervertebral disc, consisting of cartilage jacket): cells -cells die or destroy completely.Collagen structure (protein structure is based on connective tissue) fibrous rings are also interrupted.Local pain, one cannot overcome physical activity that was previously considered quite worthy.
- Stage 3. Complete destruction of fibrous rings.The adjacent vertebra stops stable.Any uncomfortable pose causes pain.Due to the experience of the nerve root that moves from the spinal cord, the limbs can be less sensitive and portable.
- 4th stage.The intervertebral disc fabric becomes a cicrricious.The vertebra may turn into a shell.The clinical evidence here depends on the individual's physiology.
Lumbar pain (lumbago) and pain that give the foot during the sciatic nerve (ishias) is one of the most common complaints that patients seek medical help.Because these symptoms are quite common in the general population, and their strong growth is also observed, the diagnosis and treatment of the patient will remain one of the key areas of neurosurgical hospital activity.Although this pathology is widespread, intervertebral disc hernia (MPD) surgery is only needed in 10% of patients with a lumbar -algia clinical picture.In other parts of patients, the best effects have conservative treatment, including drug therapy, physiotherapy training, the use of physiotherapy treatment methods, and return to physical activity a day before.
Stage of disease
The degenerative-dystrophic process most often begins with a deterioration in the intervertebral disc shock absorption function.
- The deterioration of blood supply to the intervertebral disc.In adults, intervertebral disc foods are performed by spread: blood is only conveyed to vertebrae, and has passed through them it "absorbs" to the disc.In the best way, the disc is powered during dynamic load (for example, walking), due to the principle of pump (fluid outflow processed when compressed, nutrient and oxygen flow when removing loads).Therefore, the diet of intervertebral disc is difficult especially in the state of inactive lifestyle (hypodynamia).
- Changes in pulpic disc core.With the deterioration of blood supply, water supply, sugar and amino acids to the pulpoose nucleus is disrupted.Therefore, the production of carbohydrates connects the suffering water.Nucleus dehydration, its structure made of gel -such as turning fibrous, the ability to extinguish and extinguish the shots.This increases the load on the fibrous ring and vertebrae, they are more likely to be blocked and injured.
- Changes in the intervertebral disc fibrous ring.Due to leveling the pulpoose nucleus, the increase in load lies in the fibrous disc ring.In poor blood supply, the fibrous ring loses its strength.Spinal instability occurs, which can cause the formation of intervertebral hernia, vertebral displacement and damage to the spinal cord or nerve root.
- Disk prominence.The formation of intervertebral hernia.When the fibrous ring fibers weaken, the pulpic nucleus begins to stick, for example, towards the intervertebral canal (disk protrusion).As surprising can lead to the rupture of fibrous rings and hernia formation.Read more about the process of intervertebral hernia formation in a separate article - "Effective treatment of intervertebral hernia at home".
- Spondylosis is the destruction of intervertebral joints (spondylartrosis), growth of osteophytes and ligaments.In line with the formation of intervertebral hernia in osteochondrosis, damage to the intervertebral joints, changes in vertebral (cartilage) and ligaments are observed.
As osteochondrosis and the development of complications progress, you need to use more and more frequent medicines, increasing the dose.This leads to high financial costs, as well as health deterioration due to side effects of drugs.
Drug therapy, as a rule, is supplemented by the immobilization of one or spinal cord using different orthopedic corsets -different levels of stiffness.
Surgical treatment is only allowed in cases where the stage of the spinal cord compression, which is determined by the clinical, corresponds to the examination confirming the rupture of the fibrous ring with the "loss" of the MPD hernia into the vertebral canal lumen [3-6].The results of the surgical treatment in patients with small protrusion of the disc, as a rule, are disappointed with the doctor and the patient himself.The method for establishing an accurate diagnosis is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).About 10% of the same population is impossible to run a routine MRI due to shortness of breath (fear of closed space).In this category of people, it is possible to use an "open" MRI, however, with the loss of the quality of the image obtained.Patients who had previously experienced surgical treatment were needed to conduct MRI with different reinforcement to limit postoperative scar changes from the true hernial appearance.In patients with suspected hernial MPD, when the implementation of MRI is impossible, or the results obtained are unknown, the myelography is calculated -Tomography (CT) acquires special diagnostic value.
Private diagnostic experts who interpret the results of the study, as a rule, enlarge the level of damage to the disk as a result of comparing clinical data by "finding" during tomography.Conclusions such as "Changes in accordance with the patient's age" are almost never found in the research protocol.Despite the improvement of neuroimaging techniques, the responsibility for the correct diagnosis lies in the clinical shoulder, as it can only compare the clinical picture with the data obtained during tomography.The increase in tomography resolution was slightly increased by surgical treatment, but the deviation from the norm in patients without symptoms began to detect.The process of processing the degenerative wound -Distortical spinal cord has undergone serious progress in recent years.Arthropathy of the joints is extensive in the general population and is detected quite frequently in the middle -aged and older age group during CT research. Degenerative changes in MPD, which are also widely used, quite often detected,And MRI is a more specific method for their diagnosis.At the same time, the changes mentioned in the MPD are unusual, not accompanied by a rupture of the fibrous ring, but only indicated by a slight "stabbing" the disc into the spinal canal lumen or intervertebral holes.In some cases, the degenerative process that occurs at the MPD may cause the destruction of fibrous rings with subsequent ruptures, which causes migration of part of the pulp nucleus outside the disc with the compression of the root next to the spinal cord.The claim that if the pain in the foot is observed, then it must be violated on the spinal cord root is not entirely true.For pain in the back with irradiation on the posterior surface of the thighs can cause both the MPD deterioration itself and the curved intervertebral joints.For the real attack of ishialgia caused by the compression of the MPD hernia nerve, the pain emits the posterior surface of the thighs and lower legs.Unlimited pain, limited only to the gluteal area or thigh area without distribution along the sciatic nerve, as well as bilateral pain in the gluteal or hip area that changes their localization (either on the right, then on the left), more often due to arthropathy curved joints or degeneration absorb MPD.The clinical picture of Koruska compression from the MPD hernia can also be equal pathology (for example, knee joint arthrosis).In patients with pain, surgical treatment will not have the right effect regardless of which pathology will be detected by tomography examination.In other words, in patients only with the back pain clinic, the removal of the MPD hernia will be ineffective, although the tomogram is determined by the MPD prominence, as usual and occurs.But there are also patients where the typical picture of Ishias is accompanied by disabled pain syndrome, while during a study conducted using very perception tomography, the spinal cord compression is not determined.This category of patients is not suitable for surgical intervention, from time to time, radicular symptoms, as a rule, subside.
It is necessary to clearly imagine the mechanism leading to the development of the hernial MPD to recommend to the patient the amount of movement allowed, not forgetting work activities.The power that contributes to the formation of hernial highlights is the result of degenerative changes in MPD and the second vertical decrease (height) -two fibrous rings and pulpoose nucleus.The fragments of MPD stabbed in 80% shift in the posterior direction, introducing it into the lumen of the spinal cord and the medial part of the intervertebral hole.The transfer of MPD hernia towards the midline is facilitated by the posterior longitudinal ligaments.Up to 10% of the hernial protrusion is orally or spread to the intervertebral hole (hernia forsin) or at the outer edge of the hole where the cerebrospinal spine comes out of it, thus squeezing.
In the process of essential activity, dehydration and degenerative changes cause loss of MPD height.This pathological process involves both fibrous rings and pulpic nucleus.The more significant destruction of pulpoose nucleus against the background of fibrous ring degeneration, as a rule, only leads to the loss of MPD height without significant assembly.With the main changes in the fibrous ring, the vertical force affects the preserved pulpic nucleus and their own weight, as well as the back muscles, which act on the disc in the side, cause excessive pressure on the remaining nucleus pulpoos, which cannot cancel the fibrous.
The second -second summoning leads to an increase in centrifugal pressure on the MPD, which, together with the stretching component acting on the fibrous ring fiber, can cause its rupture and fragments of the remaining pulp nucleus.After the hernial standards were formed, and the "excess" fragments of the pulp nucleus were outside the fibrous ring, the MPD structure again stable [2].As a result of the power that affects the core and fibrous rings that change from MPD, they are balanced, and their vector, which contributes to the prominence of nucleus fragments, fades.In some cases, partial degenerative changes in the pulpos nucleus contribute to the formation of gas in MPD, followed by excessive pressure on the remaining debris.The formation of hernia is also accompanied by the process of gas formation in the disc.
Excessive and sharp physical activity shown in the back of the patient, against the background of degenerative lesions -Dystrophic existing from the spine, usually only triggers leading to detailed clinical picture of compression radical syndrome, often considered by patients themselves, such as lumbar -fical -Forfial primordials.Clinically, the MPD hernia can be manifested with reflexes and compression syndrome.Syndrome is referred to compression, where the highlights of the hernial are drawn, squeezed and defective, blood vessels or spinal cord are compressed and defective.Reflex reflexes include syndrome caused by the effects of disc hernia on this structural receptor, especially the end of the spinal cord, leading to the development of reflex and tonic disorders indicated by vasomotor, distrophic, myofascial disorders.
As mentioned above, surgical treatment with degenerative lesions -Dystrophic posvinor is only advised in 10% of patients, the remaining 90% respond well for conservative steps.The basic principle of using the last is:
- relief of pain syndrome;
- Proper posture recovery to maintain the changing capacity of MPD;
- removal of muscle and tonic disorders;
- recovery of blood circulation in the roots and spinal cords;
- normalization of conductivity in nerve fibers;
- removal of cicatricial changes and distance;
- Psycho placement -somatic disorders.
Treatment
Today, in the treatment of osteochondrosis and its complications, the following group drugs are used:
- Net -ore Anti -Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) -In tablet form or drug injection.These funds have the ability to reduce pain, reduce inflammation.However, the effect of its use does not last long - from a few hours to two to three days.Therefore, such funds must be taken for a long time - weeks, and sometimes months.At the same time, these drugs negatively affect the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.Their length acceptance is full of gastritis, ulcerative lesions.In addition, they can affect kidney, liver, and contribute to the development of hypertension.And, at the same time, this fund does not contribute to the cleaning of the disc from dead cells.Therefore, its use is just one way to relieve the symptoms for a while, but does not eliminate the main problem.
- CTEPOID (GOPMONAL) anti -inflammation.As a rule, it is used for severe and irregular pain that accompanies hernia, radiculitis, ishias, and others.Gopmons has the ability to eliminate manifestations of inflammation (due to suppression of the immune system), relieving pain.But they also negatively affect the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines, promoting the release of calcium from the bone, inhibiting their own gopmon production.And does not contribute to cleaning the focus of dead cells.
- Papasmolics is a medicine that affects the muscles or nerves that go to the muscles and cause skeletal muscle relaxation.This means helping to relieve muscle clamps for a while, reducing pain and increasing blood flow.But at the same time, they do not help clean the tissue from dead cells.Therefore, they do not contribute to cure osteochondrosis.
- Epidupal block - the introduction of painkillers and goponal agents into the space between solid brain shells and periosteum covering vertebrae.It is used, as a rule, for intense pain - during the acute period of intervertebral hernia, with severe radiculitis, ishias.Depending on the composition, such injections help relieve pain for several hours to several days.After the expiration date, the manifestation of the disease is restored, as the procedure does not help restore the metabolic process in the disc.In addition, when it is performed, there is a risk of injury to the blood vessels and nerves.
Conservative treatment methods include a variety of orthopedic effects on the spine (corset immobilization, attractiveness, manual therapy), physiotherapy (therapeutic massage, physiotherapy training, acupunture, electrotherapy, mud, various heating), paravertebral, software and medicine.Degenerative wound treatment -Dystrophic spinal cord should be complex and stage.As a rule, the general principles of the Conservative Steps are the appointment of analgesic, non -stable anti -stable drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants and physiotherapy.
Analgesic effects were achieved by the appointments of diclofenac, ketoprofen, lornoxicam, tramadol.The specified analgesic and anti -Flammatory effects have loroxes, which are in both forms of injection and tablets.
NSAID is the most widely used drug for degenerative damage -Dystrophic on the spine.They have anti -antipyretic, antipyretic and antipyretic effects associated with suppression of cyclooxygenase enzymes (COC -1 and Tsos -2), which control arachidonic acid transformation into prostaglandins, prostacillas, thromboxans.In the elderly and patients with risk factors for side effects, it is advisable to carry out the "cover" of gastrotrotectors under "cover".In such patients, upon completion of NSAID injection therapy, the transition to tablets from COO -2 inhibitors, which have a lower severity of the side effects of the gastrointestinal tract, are advised.
To eliminate pain associated with increased muscle tone, it is advisable to include central muscle in complex therapy.
Degenerative lesion surgery -Dystrophic spinal cord is appropriate with non -compliance with complex conservative steps (within 2-3 weeks) in patients with MPD hernia (usually more than 10 mm) and non -prominent radicular symptoms.There are signs of emergency for surgical intervention with sequestra "fall" in the lumen of the spinal cord and express compression of the spinal cord.The development of caudal syndrome is facilitated by acute radiculomilohemia, leading to severe hyperalgia syndrome, although drug analgesic prescription, the use of restrictions (with glucocorticoid and anesthetic) does not reduce the severity of pain.It is important to note that the absolute size of the disc hernia has no determination value to make a final decision on surgical intervention and should be considered in connection with the clinical picture and is found to be detected by tomography examinations.In 95% of cases, open access to the vertebral canal is used in the hernia.Various Discovering Techniques (Coagulation Cold -Plasma, Laser reconstruction, etc.) are currently not, and their use is only allowed for MPD protrusions.The removal of classic microsurgi from disc hernia is performed using a microsurgical, binocular magnifying or operating microscope.Remote treatment results (in over 2 years) 13,359 patients undergoing the removal of MPD hernia, 6135 where sequestral was removed, and 7224 aggressive discsctomy was performed, indicating that nothing happened, known 2 times more likely (7% compared to 3.5%) in patients who only produced absorption.The quality of life is reduced more in patients with pain syndrome, while recurrent hernia formation is not always clinically indicated.
In conclusion, I will again emphasize the need for a comprehensive clinical examination and tomogram analysis to make optimal decision on tactics for specific patient care.














